


Open a new terminal and run sudo whatever, then close it and open another new terminal and run sudo whatever, you will see that sudo asks for password every time. The scenario you are experiencing is caused by the users cached credentials for sudo, which allow sudo to maintain a session and any further sudo command will not prompt for passwords. Multiple commands can be also specified for passwordless sudo usage like below.I want to run the command in user mode sudo but the terminal don't Now you can run the commands as a normal user without being prompted for a root/sudo password (and therefore, elimate the need to know the password altogether). ismail ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/passwd In the following example, the user ismail can run /bin/passwd commands with sudo without a password. All other commands with sudo will require a password too. 4 Answers Sorted by: 2 I want to run the command in user mode sudo but the terminal don't Need ask me the Password. But we can set a specific command to run with sudo without a password. Essentially, you log into the terminal with your user and password and are given a root shell. The sudo -s command grants the user a Sudo shell. By default, the NOPASSWD will disable the password for all commands with the sudo. The easiest way to run sudo commands without a password is to do it temporarily meaning no editing to the system files to change settings. %sys ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL NOPASSWD For Command or ApplicationĪnother use case for the NOPASSWD configuration is disabling the sudo password for a specific command. ismail ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL NOPASSWD For GroupĮven we have set the sudo group for passwordless sudo command let’s make a different example by setting the sys group for passwordless sudo command. In the following example, we will set the user ismail to run the sudo command without asking a password. We will just provide the username and change with the group name like below. We can also disable the sudo password for a specific user.
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL NOPASSWD For User That is the history in memory or '/.bashhistory' file.
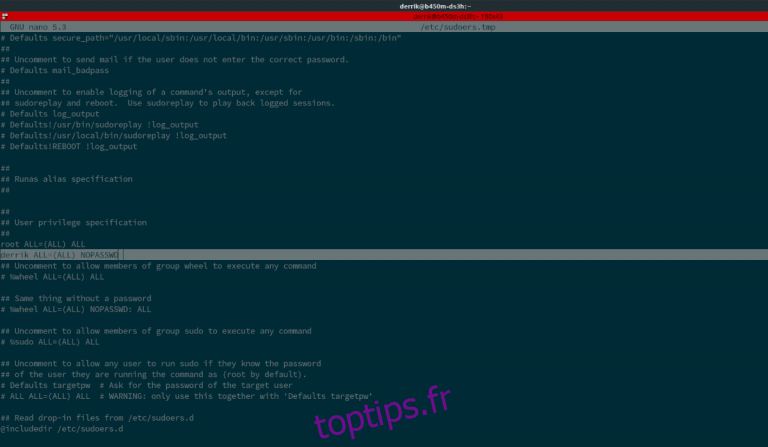
The sudoers configuration file can be opened with a command line or GUI editor but the most secure way to prevent errors and lockdowns is using the visudo command like below. Set HISTIGNORE to ' sudo -S ' export HISTIGNOREsudo -S Then pass your password safely to sudo: echo 'yourpassword' sudo -S -kIn order to make the the sudo command passwordless we should edit this file. The sudoers configuration file is used to set configuration about the sudo command. The sudo command provides the ability to run without any password which is also called as nopasswd configuration. But for heavy usage provide or typing the password is not a practical method. Execute all sudo commands without password not recommended Use the following command to edit the /etc/sudoers file: sudo visudo This will open the default text editor (Nano in Ubuntu) for editing this file. By default, the sudo command asks for the current user password to provide root privileges as a security measure.
1Modify the file To grant the permission to run commands as root users without the need of entering the password, add the following line at the end. The sudo command configuration is located in the /etc/sudoers file. 1 sudo visudo This will open a screen that looks like: 2.
The sudo command is very popular for daily usage power users generally provided the ability to run sudo command. The sudo command can be run without a password by modifying the sudoers file script withprovide the sudo command in order to execute and run a command with root privileges without logging as the root user. Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali, CentOS, RHEL, SUSE, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
